
| Free Flag Facts | ||
| Cilck here - Animated
Flag Large Static Flag |
Pakistan |

|
|
| Introduction | Pakistan |
|
Background:
|
The separation in 1947 of British India into the Muslim state of Pakistan (with two sections West and East) and largely Hindu India was never satisfactorily resolved. A third war between these countries in 1971 resulted in East Pakistan seceding and becoming the separate nation of Bangladesh. A dispute over the state of Kashmir is ongoing. In response to Indian nuclear weapons testing, Pakistan conducted its own tests in 1998. |
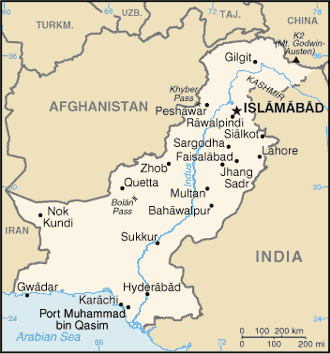
| Geography | Pakistan |
|
Location:
|
Southern Asia, bordering the Arabian Sea, between India on the east and Iran and Afghanistan on the west and China in the north |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
30 00 N, 70 00 E |
|
Map references:
|
Asia |
|
Area:
|
total: 803,940 sq km
land: 778,720 sq km water: 25,220 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly less than twice the size of California |
|
Land boundaries:
|
total: 6,774 km
border countries: Afghanistan 2,430 km, China 523 km, India 2,912 km, Iran 909 km |
|
Coastline:
|
1,046 km |
|
Maritime claims:
|
contiguous zone: 24 NM
territorial sea: 12 NM continental shelf: 200 NM or to the edge of the continental margin exclusive economic zone: 200 NM |
|
Climate:
|
mostly hot, dry desert; temperate in northwest; arctic in north |
|
Terrain:
|
flat Indus plain in east; mountains in north and northwest; Balochistan plateau in west |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m
highest point: K2 (Mt. Godwin-Austen) 8,611 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
land, extensive natural gas reserves, limited petroleum, poor quality coal, iron ore, copper, salt, limestone |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 27.81%
permanent crops: 0.79% other: 71.4% (1998 est.) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
180,000 sq km (1998 est.) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
frequent earthquakes, occasionally severe especially in north and west; flooding along the Indus after heavy rains (July and August) |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
water pollution from raw sewage, industrial wastes, and agricultural runoff; limited natural fresh water resources; a majority of the population does not have access to potable water; deforestation; soil erosion; desertification |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Marine Life Conservation, Nuclear Test Ban |
|
Geography - note:
|
controls Khyber Pass and Bolan Pass, traditional invasion routes between Central Asia and the Indian Subcontinent |
| People | Pakistan |
|
Population:
|
150,694,740 (July 2003 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 39.3% (male 30,463,958; female 28,726,776)
15-64 years: 56.5% (male 43,571,093; female 41,651,872) 65 years and over: 4.2% (male 3,051,674; female 3,229,367) (2003 est.) |
|
Median age:
|
total: 19.8 years
male: 19.7 years female: 20 years (2002) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
2.01% (2003 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
29.59 births/1,000 population (2003 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
8.79 deaths/1,000 population (2003 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
-0.75 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2003 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.06 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 1.05 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.94 male(s)/female total population: 1.05 male(s)/female (2003 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 76.53 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 76.09 deaths/1,000 live births (2003 est.) male: 76.95 deaths/1,000 live births |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 62.2 years
male: 61.3 years female: 63.14 years (2003 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
4.1 children born/woman (2003 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
0.1% (2001 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
78,000 (2001 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
4,500 (2001 est.) |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: Pakistani(s)
adjective: Pakistani |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
Punjabi, Sindhi, Pashtun (Pathan), Baloch, Muhajir (immigrants from India at the time of partition and their descendants) |
|
Religions:
|
Muslim 97% (Sunni 77%, Shi'a 20%), Christian, Hindu, and other 3% |
|
Languages:
|
Punjabi 48%, Sindhi 12%, Siraiki (a Punjabi variant) 10%, Pashtu 8%, Urdu (official) 8%, Balochi 3%, Hindko 2%, Brahui 1%, English (official and lingua franca of Pakistani elite and most government ministries), Burushaski, and other 8% |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 45.7% male: 59.8% female: 30.6% (2003 est.) |
| Government | Pakistan |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: Islamic Republic of Pakistan
conventional short form: Pakistan former: West Pakistan |
|
Government type:
|
federal republic |
|
Capital:
|
Islamabad |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
4 provinces, 1 territory*, and 1 capital territory**; Balochistan, Federally Administered Tribal Areas*, Islamabad Capital Territory**, North-West Frontier Province, Punjab, Sindh
note: the Pakistani-administered portion of the disputed Jammu and Kashmir region includes Azad Kashmir and the Northern Areas |
|
Independence:
|
14 August 1947 (from UK) |
|
National holiday:
|
Republic Day, 23 March (1956) |
|
Constitution:
|
10 April 1973, suspended 5 July 1977, restored with amendments 30 December 1985; suspended 15 October 1999, restored on 31 December 2002
note: selected provisions of the Constitution pertaining to changes President MUSHARRAF made while the Constitution was suspended, remain contested by political opponents |
|
Legal system:
|
based on English common law with provisions to accommodate Pakistan's status as an Islamic state; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction, with reservations |
|
Suffrage:
|
18 years of age; universal; joint electorates and reserved parliamentary seats for women and non-Muslims |
|
Executive branch:
|
note: following a military takeover on 12 October 1999, Chief of Army Staff and Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff Committee, General Pervez MUSHARRAF, suspended Pakistan's constitution and assumed the additional title of Chief Executive; exercising the powers of the head of the government, he appointed an eight-member National Security Council to function as Pakistan's supreme governing body; on 12 May 2000, Pakistan's Supreme Court unanimously validated the October 1999 coup and granted MUSHARRAF executive and legislative authority for three years from the coup date; on 20 June 2001, MUSHARRAF named himself as president and was sworn in, replacing Mohammad Rafiq TARAR; in a referendum held on 30 April 2002, MUSHARRAF's presidency was extended by five more years
chief of state: President Pervez MUSHARRAF (since 20 June 2001) head of government: Prime Minister Mir Zafarullah Khan JAMALI (since 23 November 2002) elections: the president is elected by Parliament for a five-year term; note - in a referendum held on 30 April 2002, MUSHARRAF's presidency was extended by five more years (next to be held NA 2007); the prime minister is selected by the National Assembly for a four-year term (next to be held NA 2006) election results: results are for the 10 October 2002 election for prime minister - Mir Zafarullah Khan JAMALI elected prime minister cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the Prime Minister |
|
Legislative branch:
|
bicameral Parliament or Majlis-e-Shoora consists of the Senate (100 seats - formerly 87; members indirectly elected by provincial assemblies to serve four-year terms; and the National Assembly (342 seats - formerly 217; 60 seats represent women; 10 seats represent minorities; members elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms)
election results: Senate results - percent of vote by party - NA%; seats by party - PML/Q 40, PPPP 11, MMA 21, MQM/A 6, PML/N 4, NA 3, PML/F 1, PkMAP 2, ANP 2, PPP/S 2, JWP 1, BNP-Awami 1, BNP-Mengal 1, BNM/H 1, independents 4; National Assembly results - percent of votes by party - NA%; seats by party - PML/Q 126, PPPP 81, MMA 63, PML/N 19, MQM/A 17, NA 16, PML/F 5, PML/J 3, PPP/S 2, BNP 1, JWP 1, PAT 1, PML/Z 1, PTI 1, MQM/H 1, PkMAP 1, independents 3 elections: Senate - last held 24 and 27 February 2003 (next to be held by February 2007); National Assembly - last held 10 October 2002 (next to be held by October 2006) |
|
Judicial branch:
|
Supreme Court (justices appointed by the president); Federal Islamic or Shari'a Court |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
Awami National Party or ANP [Wali KHAN]; Balochistan National Movement/Hayee Group or BNM/H [Dr. Hayee BALUCH]; Baluch National Party or BNP [Sardar Akhtar MENGAL]; Baluch National Party/Awami or BNP/Awami [Moheem Kahn BALOCH]; Jamhoori Watan Party or JWP [Akbar Khan BUGTI]; Jamiat-al-Hadith or JAH [Sajid MIR]; Jamiat Ulema-i-Islam, Fazlur Rehman faction or JUI/F [Fazlur REHMAN]; Jamiat Ulema-i-Islam, Sami-ul-HAQ faction or JUI/S [Sami ul-HAQ]; Jamiat-i-Islami or JI [Qazi Hussain AHMED]; Jamiat Ulema-i-Pakistan, Noorani faction or JUP/NO [Shah Ahmad NOORANI]; Millat Party or MP [Farooq LEGHARI]; Mutahida Qaumi Movement, Altaf faction or MQM/A [Altaf HUSSAIN]; Muhajir Quami Movement, Haqiqi faction or MQM/H [Afaq AHMAD]; Muttahida Majlis-e-Amal Pakistan or MMA [leader NA]; National Alliance or NA [Farooq Ahmad Khan LEGHARI]; National People's Party or NPP [Ghulam Mustapha JATOI]; Pakhtun Khwa Milli Awami Party or PkMAP [Mahmood Khan ACHAKZAI]; Pakhtun Quami Party or PQP [Mohammed Afzal KHAN]; Pakistan Awami Tehrik or PAT [Tahir ul QADRI]; Pakistan Democratic Party or PDP [Nawabadzada KHAN]; Pakistan Muslim League, Functional Group or PML/F [Pir PAGARO]; Pakistan Muslim League, Junejo faction or PML/J [Hamid Nasir CHATTHA]; Pakistan Muslim League, Nawaz Sharif faction or PML/N [Nawaz SHARIF]; Pakistan Muslim League, Quaid-l-Azam faction or PML/Q [Chaudhry Shujjat HUSSEIN]; Pakistan Muslim League, Zia-ul-HAQ or PML/Z [Ejaz ul-Haq]; Pakistan National Party or PNP [Hasil BIZENJO]; Pakistan People's Party or PPP [Benazir BHUTTO]; Pakistan People's Party/Sherpao or PPP/S [Aftab Ahmed Khan SHERPAO]; Pakistan People's Party/Shaheed Bhutto or PPP/SB [Ghinva BHUTTO]; Pakistan People's Party Parliamentarians or PPPP [Amin FAHIM]; Pakistan Tehrik-e-Insaaf or PTI [Imran KHAN]; Tehrik-i-Islami [Allama Sajid NAQVI]; Tehrik-i-Insaaf or PTI [Imran KHAN]
note: political alliances in Pakistan can shift frequently |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
military remains most important political force; ulema (clergy), landowners, industrialists, and small merchants also influential |
|
International organization participation:
|
AsDB, ASEAN (dialogue partner), C (suspended), CP, ECO, ESCAP, FAO, G-19, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICFTU, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ISO, ITU, MINURSO, MONUC, NAM, OAS (observer), OIC, OPCW, PCA, SAARC, UN, UN Security Council (temporary), UNAMSIL, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIKOM, UNITAR, UNMIBH, UNMIK, UNMISET, UNMOP, UNOMIG, UPU, WCL, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WToO, WTrO |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Ashraf Jehangir QAZI
chancery: 2315 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008 FAX: [1] (202) 387-0484 consulate(s) general: Los Angeles, New York, and Sunnyvale (California) telephone: [1] (202) 939-6205 |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Nancy J. POWELL
embassy: Diplomatic Enclave, Ramna 5, Islamabad mailing address: P. O. Box 1048, Unit 62200, APO AE 09812-2200 telephone: [92] (51) 2080-0000 FAX: [92] (51) 2276427 consulate(s): Karachi, Lahore, Peshawar |
|
Flag description:
|
green with a vertical white band (symbolizing the role of religious minorities) on the hoist side; a large white crescent and star are centered in the green field; the crescent, star, and color green are traditional symbols of Islam |
| Economy | Pakistan |
|
Economy - overview:
|
Pakistan, an impoverished and underdeveloped country, suffers from internal political disputes, low levels of foreign investment, and a costly, ongoing confrontation with neighboring India. Pakistan's economic prospects, although still marred by poor human development indicators, continued to improve in 2002 following unprecedented inflows of foreign assistance beginning in 2001. Foreign exchange reserves have grown to record levels, supported largely by fast growth in recorded worker remittances. Trade levels rebounded after a sharp decline in late 2001. The government has made significant inroads in macroeconomic reform since 2000, but progress is beginning to slow. Although it is in the second year of its $1.3 billion IMF Poverty Reduction and Growth Facility, Islamabad continues to require waivers for politically difficult reforms. Long-term prospects remain uncertain as development spending remains low, regional tensions remain high, and political tensions weaken Pakistan's commitment to lender-recommended economic reforms. GDP growth will continue to hinge on crop performance; dependence on foreign oil leaves the import bill vulnerable to fluctuating oil prices; and efforts to open and modernize the economy remain uneven. |
|
GDP:
|
purchasing power parity - $295.3 billion (2002 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
4.4% (FY01/02 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita:
|
purchasing power parity - $2,000 (FY01/02 est.) |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 24%
industry: 25% services: 51% (FY01/02 est.) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
35% (2001 est.) |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: 4.1%
highest 10%: 27.6% (1996-97) |
|
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
|
41 (FY98/99) |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
3.9% (2002 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
40.4 million
note: extensive export of labor, mostly to the Middle East, and use of child labor (2000) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
agriculture 44%, industry 17%, services 39% (1999 est.) |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
7.8% plus substantial underemployment (2002 est.) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $12.6 billion
expenditures: $14.8 billion, including capital expenditures of $NA (FY02/03 est.) |
|
Industries:
|
textiles, and apparel, food processing, beverages, construction materials, paper products, fertilizer, shrimp |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
2.4% (FY01/02 est.) |
|
Electricity - production:
|
66.96 billion kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - production by source:
|
fossil fuel: 68.8%
hydro: 28.2% other: 0% (2001) nuclear: 3% |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
62.27 billion kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
0 kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
0 kWh (2001) |
|
Oil - production:
|
62,870 bbl/day (2001 est.) |
|
Oil - consumption:
|
365,000 bbl/day (2001 est.) |
|
Oil - exports:
|
NA (2001) |
|
Oil - imports:
|
NA (2001) |
|
Oil - proved reserves:
|
297.1 million bbl (37257) |
|
Natural gas - production:
|
23.4 billion cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - consumption:
|
23.4 billion cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - exports:
|
0 cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - imports:
|
0 cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - proved reserves:
|
695.6 billion cu m (37257) |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
cotton, wheat, rice, sugarcane, fruits, vegetables; milk, beef, mutton, eggs |
|
Exports:
|
$9.8 billion f.o.b. (FY02/03 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
textiles (garments, cotton cloth, and yarn), rice, leather, sports goods, and carpets and rugs |
|
Exports - partners:
|
US 24.5%, UAE 8.5%, UK 7.2%, Germany 4.9%, Hong Kong 4.8% (2002) |
|
Imports:
|
$11.1 billion f.o.b. (FY02/03 est.) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
petroleum, petroleum products, machinery, chemicals, transportation equipment, edible oils, pulses, iron an steel, tea |
|
Imports - partners:
|
UAE 11.7%, Saudi Arabia 11.7%, Kuwait 6.7%, US 6.4%, China 6.2%, Japan 6%, Malaysia 4.5%, Germany 4.4% (2002) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$32.3 billion (2002 est.) |
|
Economic aid - recipient:
|
$2.4 billion (FY01/02) |
|
Currency:
|
Pakistani rupee (PKR) |
|
Currency code:
|
PKR |
|
Exchange rates:
|
Pakistani rupees per US dollar - 59.72 (2002), 61.93 (2001), 53.65 (2000), 49.12 (1999), 44.94 (1998) |
|
Fiscal year:
|
1 July - 30 June |
| Communications | Pakistan |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
2.861 million (March 1999) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
158,000 (1998) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: the domestic system is mediocre, but improving; service is adequate for government and business use, in part because major businesses have established their own private systems; since 1988, the government has promoted investment in the national telecommunications system on a priority basis, significantly increasing network capacity; despite major improvements in trunk and urban systems, telecommunication services are still not readily available to the majority of the rural population
domestic: microwave radio relay, coaxial cable, fiber-optic cable, cellular, and satellite networks international: satellite earth stations - 3 Intelsat (1 Atlantic Ocean and 2 Indian Ocean); 3 operational international gateway exchanges (1 at Karachi and 2 at Islamabad); microwave radio relay to neighboring countries (1999) |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 27, FM 1, shortwave 21 (1998) |
|
Radios:
|
13.5 million (1997) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
22 (plus seven low-power repeaters) (1997) |
|
Televisions:
|
3.1 million (1997) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.pk |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
30 (2000) |
|
Internet users:
|
1.2 million (2000) |
| Transportation | Pakistan |
|
Railways:
|
total: 8,163 km
broad gauge: 7,718 km 1.676-m gauge (293 km electrified) narrow gauge: 445 km 1.000-m gauge (2002) |
|
Highways:
|
total: 254,410 km
paved: 109,396 km (including 339 km of expressways) unpaved: 145,014 km (1999) |
|
Waterways:
|
none |
|
Pipelines:
|
gas 9,945 km; oil 1,821 km (2003) |
|
Ports and harbors:
|
Karachi, Port Muhammad bin Qasim |
|
Merchant marine:
|
total: 18 ships (1,000 GRT or over) 247,675 GRT/375,435 DWT
ships by type: cargo 14, container 3, petroleum tanker 1 (2002 est.) |
|
Airports:
|
124 (2002) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 87
over 3,047 m: 14 2,438 to 3,047 m: 21 914 to 1,523 m: 17 under 914 m: 3 (2002) 1,524 to 2,437 m: 32 |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 37
1,524 to 2,437 m: 9 914 to 1,523 m: 9 under 914 m: 19 (2002) |
|
Heliports:
|
13 (2002) |
| Military | Pakistan |
|
Military branches:
|
Army, Navy, Air Force, Civil Armed Forces, National Guard |
|
Military manpower - military age:
|
17 years of age (2003 est.) |
|
Military manpower - availability:
|
males age 15-49: 38,133,733 (2003 est.) |
|
Military manpower - fit for military service:
|
males age 15-49: 23,328,575 (2003 est.) |
|
Military manpower - reaching military age annually:
|
males: 1,767,502 (2003 est.) |
|
Military expenditures - dollar figure:
|
$2.964 billion (FY02) |
|
Military expenditures - percent of GDP:
|
4.6% (FY02) |
| Transnational Issues | Pakistan |
|
Disputes - international:
|
thousands of Afghan refugees still reside in Pakistan; isolating terrain and close ties among Pashtuns in Pakistan make cross-border activities difficult to control; armed stand-off with India over the status and sovereignty of Kashmir continues - India objects to Pakistan ceding lands to China in 1965 boundary agreement that India believes are part of disputed Kashmir; disputes with India over Indus River water sharing and the terminus of the Rann of Kutch, which prevents maritime boundary delimitation |
|
Illicit drugs:
|
opium poppy cultivation practically eliminated; key transit point for Southwest Asian heroin bound for Western markets; Afghan narcotics continue to transit Federally Administered Tribal Areas, Balochistan Province, and Karachi; financial crimes related to drug trafficking, terrorism, corruption, and smuggling remain problems |